Se all' interno della tua pennetta USB il tuo Tails non si avvia, riferisciti alle istruzioni su recupero dei dati dallo Storage Persistente quando Tails non si avvia.
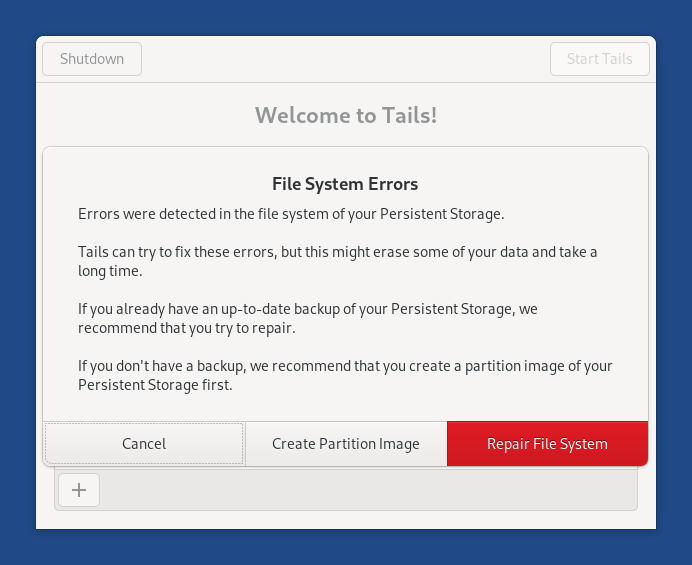
Tails può provare a risolvere questi errori,ma questo cancellerà alcuni dati e richiederà molto tempo
Questo è il perché, sé non puoi riottenere dal recente backup il tuo sistema operativo, ti raccomandiamo di creare una immagine partizione della tua storage persistente dopo prova a riparare il file system della tua Storage Persistente dalla schermata di Benvenuto.
Molte dell volte, riparare il file system funziona nella maggior parte dei casi per risolvere lo Storage Persistente
Nei casi più rari quando ripari il file system non funziona, potresti voler recuperare alcuni o molti dei tuoi dati della tua immagine di partizione utilizzando strumenti avanzati forensi. Tuttavia questo processo di recupero e veramente tecnico è potresti voler chiedere aiuto da qualcuno che ha più esperienza senza cip recupero dati
- Recupero dei dati dall'Archivio Persistente quando presenta errori di file system.
- Crea una immagine di partizione dal tuo Storage Persistente
- Recovering data from the Persistent Storage
Crea una immagine di partizione dal tuo Storage Persistente
Una immagine di partizione è una copia del tuo intero Storage Persistente in un singolo file che puoi salvare in un Disco Rigido esterno proveniente da Tails
Per salvare l'immagine della partizione al di fuori di Tails, hai bisogno di un disco rigido esterno con tanto spazio libero quanto la dimensione del tuo Archivio Persistente, di solito 8 GB in meno rispetto alla tua chiavetta USB Tails. Puoi anche utilizzare un'altra chiavetta USB della stessa dimensione della tua chiavetta USB Tails, ma scrivere su una chiavetta USB è di solito molto più lento rispetto a scrivere su un disco rigido.
L'immagine della partizione contiene una versione decriptato del tuo Archivio Persistente.
Ti consigliamo di salvare l'immagine della partizione su un disco rigido cifrato
Presentiamo qui 2 diverse tecniche per creare un'immagine di partizione del tuo Archivio Persistente.
Crea una partizione usando l'utilità Dischi
Prova prima questa tecnica se l'hardware della tua chiavetta USB non sta riuscendo.
Crea un'immagine di partizione usando
ddrescuesulla riga di comandoProva prima questa tecnica se l'hardware della tua chiavetta USB non ci riesce.
Usare
ddrescueè più difficile ma è meglio dell'utilità Disks per recuperare dati se l'hardware della tua chiavetta USB snon riesce.
Creare un'immagine di partizione utilizzando l'utilità Dischi
Quando l'hardware della tua chiavetta USB non è guasto, utilizzare l'utilità Disks è il modo più semplice per creare un'immagine di partizione del tuo Archivio Persistente.
Preparazione del disco rigido esterno
Avvia Tails.
Nella schermata di benvenuto:
Scegli di avviare senza sbloccare il tuo Archivio Persistente.
Choose Applications ▸ Files to open the Files browser.
Collega il disco rigido su cui vuoi salvare l'immagine della partizione del tuo Archivio Persistente. Hai bisogno di tanto spazio libero quanto la dimensione del tuo Archivio Persistente, di solito 8 GB in meno rispetto alla tua chiavetta USB Tails.
Un nuovo disco compare nella barra laterale dell'utilità File.
Clicca con il tasto destro (su Mac, clicca con due dita) sul nuovo volume comparso nella barra laterale dell'utilità File e scegli Proprietà nel menu di scelta rapida.
Prendi nota dello spazio libero nel disco.
Identificare il tuo Archivio Persistente nell'utilità Dischi
Scegli Applicazioni ▸ Utility ▸ Dischi per aprire l'utilità Dischi.
Nel riquadro sinistro dell'utilità Disks, identifica la tua chiavetta USB Tails nell'elenco dei dispositivi di archiviazione.
Verifica la sua marca e dimensione.
Nel riquadro sinistro, clicca sul dispositivo di archiviazione che corrisponde alla tua chiavetta USB Tails.
Nel riquadro di destra, questo dispositivo di archiviazione dovrebbe avere 2 volumi, corrispondenti a 2 partizioni sulla chiavetta USB.
1 volume con etichetta TAILS e contenuto FAT.
Questo volume corrisponde alla partizione di sistema del tuo Tails.
1 volume con etichetta TailsData e contenuto LUKS.
Questo volume corrisponde alla versione cifrata del tuo Archivio Persistente.

Nel riquadro di destra, clicca sul volume che corrisponde al tuo Archivio Persistente.
Verifica che il contenuto del volume sia di tipo Crittografia LUKS.
Sbloccare l'Archivio Persistente nell'utilità Dischi
Prima di creare l'immagine della partizione, sblocca la crittografia per accedere alla versione decrittata del tuo Archivio Persistente. Per farlo:
Clicca su
 .
.Nella finestra di dialogo Inserisci la frase d'accesso per sbloccare, inserisci la frase d'accesso del tuo Archivio Persistente.
Clicca Sblocca.
Nella finestra di dialogo Autenticazione richiesta, inserisci la tua password di amministrazione.
Se lo sblocco fallisce in questo passaggio, il tuo Archivio Persistente è così danneggiato che la decrittazione è impossibile, rendendo tutti i tuoi dati completamente irrecuperabili.
Nel riquadro di destra, clicca sul nuovo volume che compare sotto il volume LUKS.
Verifica che il contenuto del nuovo volume sia di tipo Ext4.
Questo volume corrisponde alla versione decrittata del tuo Archivio Persistente.
Verifica che la dimensione del tuo Archivio Persistente decrittato sia inferiore allo spazio libero disponibile nel disco rigido esterno.
Prendi nota del nome del dispositivo del tuo Archivio Persistente.
Il nome del dispositivo è composto da
/dev/mapper/luks, seguito da lettere e numeri.
Creazione dell'immagine della partizione
Seleziona
 ▸ Crea immagine della
partizione.
▸ Crea immagine della
partizione.Nella finestra di dialogo Crea immagine disco:
Nel campo Nome, specifica persistent-storage.img.
Nel menu Salva nella cartella, seleziona il disco esterno su cui desideri salvare l'immagine della partizione.
Clicca sul pulsante Inizia a Creare
Nella finestra di dialogo Autenticazione richiesta, inserisci la tua password di amministrazione.
Dopo che la creazione dell'immagine della partizione è completata:
Se è stata creata con successo, spegni Tails.
You can now safely start recovering data from the Persistent Storage.
If the creation failed, try the second technique described below to create a partition image using
ddrescueon the command line instead.
Creating a partition image using ddrescue on the command line
If creating a partition image using the Disks utility fails, you can try
this second technique using ddrescue, which can be more resilient to
hardware failures.
The ddrescue utility tries to copy first the parts of the Persistent
Storage that are not failing and skips over the parts that are
failing. After that, you can run ddrescue again to try to copy the parts
that failed the first time.
Scegli Applicazioni ▸ File per aprire l'utilità File.
In the Files utility, navigate to the folder of the external hard where you want to save the partition image of your Persistent Storage.
Right-click in the empty space of the right pane and choose Open in Terminal in the shortcut menu.
Doing so opens a terminal that is configured to operate in this folder.
In the terminal, execute the following command. Replace /dev/mapper/luks-xyz with the device name found when identifying your Persistent Storage in the Disks utility.
ddrescue /dev/mapper/luks-xyz persistent-storage.img ddrescue.log
The output of
ddrescuelooks like this:GNU ddrescue 1.27 Press Ctrl-C to interrupt ipos: 749404 kB, non-trimmed: 0 B, current rate: 34996 kB/s ipos: 1446 MB, non-trimmed: 0 B, current rate: 24772 kB/s opos: 1446 MB, non-scraped: 0 B, average rate: 33629 kB/s non-tried: 9290 MB, bad-sector: 0 B, error rate: 0 B/s rescued: 1446 MB, bad areas: 0, run time: 43s pct rescued: 13.46%, read errors: 0, remaining time: 1m 31s time since last successful read: 0s Copying non-tried blocks... Pass 1 (forwards)The section about bad areas refers to errors reading the data of your Persistent Storage, most likely because of hardware failures.
After
ddrescuefinishes:If bad areas were reported, try leaving your USB stick to rest for some minutes and executing the same
ddrescuecommand again to copy more data.We recommend that you replace your USB stick and copy the partition image to a new USB stick after you execute
ddrescueseveral times.If no bad areas were reported or if the same bad areas were reported after several executions of the
ddrescuecommand, it means that all the data that could be rescued was copied to the partition image.
Shut down Tails.
You can now safely start recovering data from the Persistent Storage.
Recovering data from the Persistent Storage
After creating a partition image, you can safely try to recover data from your Persistent Storage without risking erasing more data.
We are presenting here 3 recovery techniques that work in different cases. We recommend that you try the 3 techniques one after the other.
Repairing the file system from the Welcome Screen
If the hardware of your USB stick is not failing, repairing the file system from the Welcome Screen is likely the easiest technique.
Copying the partition image to a new USB stick
If the hardware of your USB stick is failing, you might still be able to repair the file system of your Persistent Storage after copying the partition image to a new USB stick.
Analyzing the partition image using Autopsy
Autopsy is an advanced digital forensics tool that allows recovering files, even from broken file systems.
Repairing the file system from the Welcome Screen
If the hardware of your USB stick is not failing, repairing the file system from the Welcome Screen is likely the easiest technique.
Start on the Tails USB stick that has file system errors.
In the Welcome Screen, try to unlock the Persistent Storage.
When the error message about file system errors appears, click on the Repair File System button.

The repair of the file system starts.
The repair can take a long time, from a few seconds to several hours.
If the repair takes more than a day, shutdown Tails and try analyzing the partition image using Autopsy instead.

After the repair finishes:
If the repair succeeded, start Tails and verify the content of your Persistent Storage.
We recommend that you keep the partition image for some time.
If you realize later on that some files are missing or damaged, you might be able to recover them by analyzing the partition image using Autopsy.
If the repair failed, try to copy the partition image to a new USB stick as described below.
Copying the partition image to a new USB stick
If the hardware of your USB stick is failing, you might still be able to repair the file system of your Persistent Storage after copying the partition image to a new USB stick.
Creating a new Tails USB stick with Persistent Storage
Install Tails on a new USB stick.
The new USB stick must be at least as large as your current Tails USB stick.
Start on the new Tails.
When starting Tails, set up an administration password.
Create a Persistent Storage on the new Tails.
Close the Persistent Storage settings after creation, when the list of features is displayed.
The process described below overwrites the contents and configuration of the new Persistent Storage. So, it does not matter which features you turn on after creating the Persistent Storage.
Copying the partition image onto the new USB stick
Scegli Applicazioni ▸ Utility ▸ Dischi per aprire l'utilità Dischi.
In the left pane of the Disks utility, identify your new Tails USB stick in the list of storage devices.
Verifica la sua marca e dimensione.
In the left pane, click on the storage device that corresponds to your new Tails USB stick.
In the right pane, this storage device should have 3 volumes.
1 volume con etichetta TAILS e contenuto FAT.
Questo volume corrisponde alla partizione di sistema del tuo Tails.
1 volume con etichetta TailsData e contenuto LUKS.
Questo volume corrisponde alla versione cifrata del tuo Archivio Persistente.
1 volume with a TailsData label and Ext4 content.
This volume corresponds to the decrypted version of your Persistent Storage.
In the right pane, click on the Ext4 volume, which is the one that corresponds to the decrypted version of your Persistent Storage.
In the attributes listed below the volume, verify that the content of the volume is mounted at /home/amnesia/Persistent.
Click on the
 button to unmount the
Persistent Storage.
button to unmount the
Persistent Storage.Plug in the hard disk on which you saved the partition image of your Persistent Storage.
Choose
 ▸ Restore Partition Image.
▸ Restore Partition Image.In the Restore Disk Image dialog, browse for the partition image on the hard disk that you plugged in.
Click on the Start Restoring button.
After the restoration finishes, restart on the new Tails USB stick.
Fixing the file system errors on the new USB stick
In the Welcome Screen, try to unlock the Persistent Storage.
If an error message about file system errors appears, click on the Repair File System button.

The repair of the file system starts.
The repair can take a long time, from a few seconds to several hours.
If the repair takes more than a day, shutdown Tails and try analyzing the partition image using Autopsy instead.

After the repair finishes:
If the repair succeeded, start Tails and verify the content of your Persistent Storage.
We recommend that you keep the partition image for some time.
If you realize later on that some files are missing or damaged, you might be able to recover them by analyzing the partition image using Autopsy.
If the repair failed, try to analyze the partition image using Autopsy as described below.
Analyzing the partition image using Autopsy
Autopsy is an advanced digital forensics tool that allows recovering files, even from broken file systems.
Autopsy is open source and available for free on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
To avoid leaving traces of the content of your Persistent Storage on the operating system where Autopsy is used, we recommend that you use Autopsy in Tails. But, Autopsy is easier to install in Windows than in Tails.
We are not providing step-by-step instructions on how to install and use Autopsy.
If you don't feel confident installing and using Autopsy on your own, we recommend that you get help from someone with more experience with Linux and data recovery.
You can also read the Autopsy User Documentation.
Installing Autopsy in Tails
The general steps are:
From the download page, download the 2 binaries needed to run Autopsy:
The DEB file of The Sleuth Kit.
The ZIP file of Autopsy.
From the installation instructions of Autopsy for Linux, download the 2 scripts needed for the installation:
install_prereqs_ubuntu.shinstall_application.sh
Execute the following commands in a Terminal. You might have to adjust to newer versions of Autopsy.
bash install_prereqs_ubuntu.sh
sudo apt install libsqlite3-dev libc3p0-java unzip
sudo dpkg -i sleuthkit-java_4.12.1-1_amd64.deb
bash install_application.sh -z autopsy-4.21.0.zip -i ~/Persistent/autopsy -j /usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-amd64
/home/amnesia/Persistent/autopsy/autopsy-4.21.0/bin/autopsy
When starting for the first time, Autopsy freezes on Starting modules.
Press Enter to continue.
Using Autopsy to analyze the partition image
The general steps are:
Start Autopsy.
Open a new case.
Add the partition image of the Persistent Storage as a data source.
Autopsy analyzes the data source.
After the analysis finishes, the files that were recovered are listed in different ways in the left sidebar, for example, both as a file system tree and by type of files.
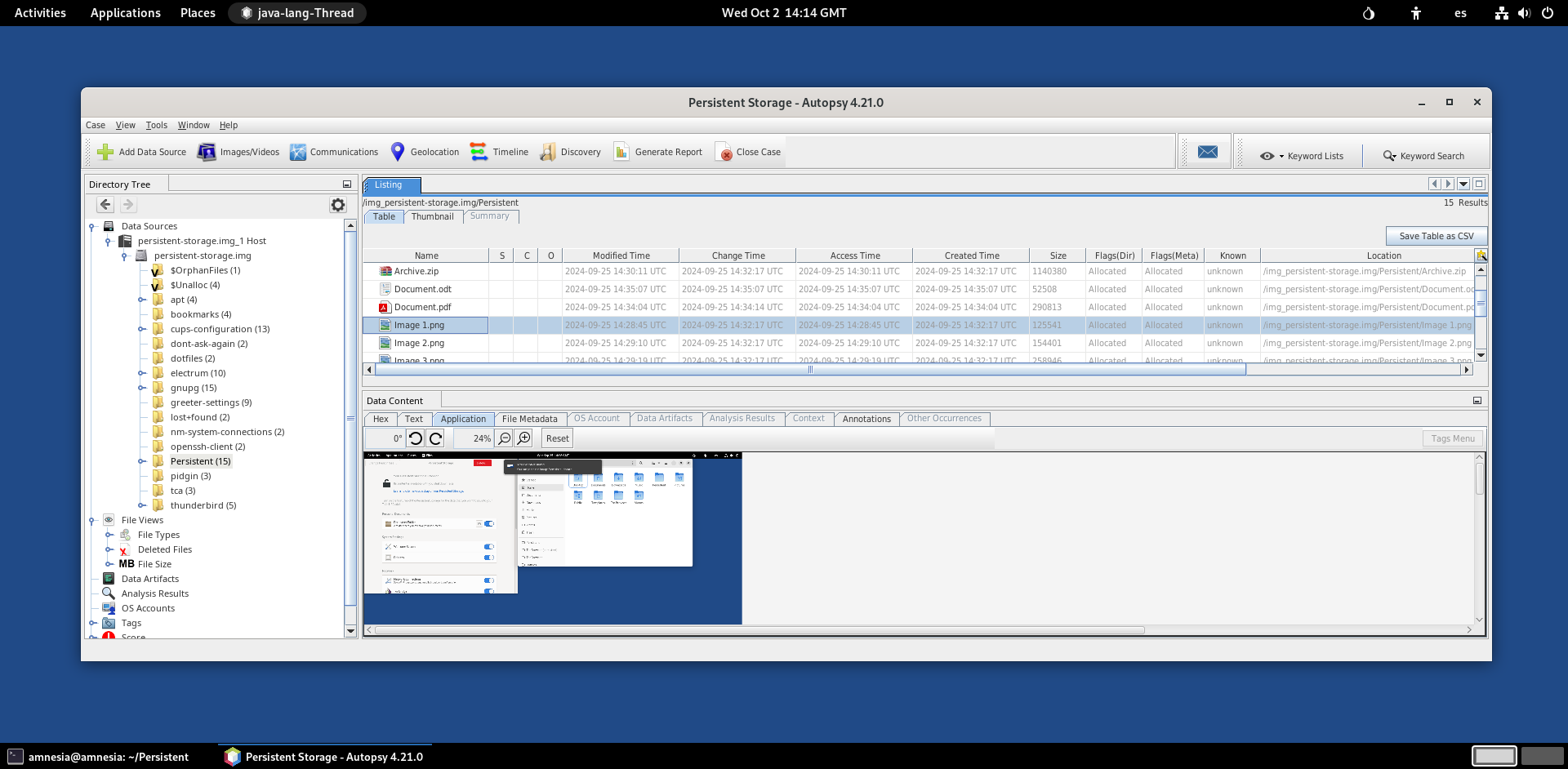
Extract the files that you want to recover to the case folder.